2024-07-03
Staying dirty during the printing process is a common problem, but it is a complex and systematic problem. Staying dirty during printing is related to the quality of the printing plate, the state of the printing machine, the printing process, substrate, ink, and plate lubricant. Staying dirty during printing directly affects the quality of the printed product, causing waste and reducing user work efficiency. Especially, the target of purple laser CTP plates is mainly newspapers, and the printing and publishing of newspapers have extremely high requirements for work efficiency. Therefore, accurately determining the cause of printing dirty and taking corresponding measures to avoid or solve it can ensure the efficient progress of the printing process.
This article introduces the purple laser CTP plate and the post-processing process of the plate. Then, from the quality of the plate and the exposure and development process, it analyzes the possible reasons and solutions for dirty printing using purple laser plates.
1. Purple laser CTP plate material
Purple laser CTP plate material is a negative pattern plate material that uses photopolymerization as the imaging mechanism. The plate-making equipment is a CTP plate-making machine that uses a 405nm wavelength purple laser diode as the light source. Compared to the PS and thermal CTP versions, the purple laser CTP version has a higher sensitivity and must be manually operated in a safe light (amber light) environment. It is prohibited to use it under white light conditions.
After being exposed to a 405nm wavelength laser, the photosensitive layer in the exposed area of the purple laser CTP plate undergoes a polymerization reaction and solidifies. It changes from easily soluble to insoluble in the special development solution for the purple laser plate (hereinafter referred to as the development solution). The unexposed area is removed after development processing, forming a blank area of the printing plate. The exposed area solidifies and remains, forming a printing plate image and text area. The schematic diagram of its plate-making process and plate-making principle is shown in Figure 1: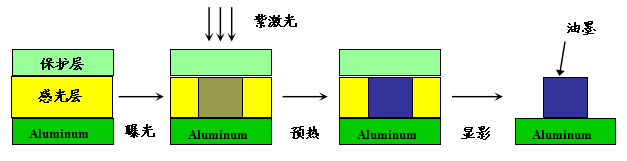
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of photopolymerization CTP plate making
During the exposure stage, the sensitizing dye in the photosensitive layer absorbs laser energy, causing molecules to transition from the ground state to the excited state. Through energy or electron transfer, the initiator is sensitized and decomposed to produce free radicals, triggering polymerization and solidification of the active groups in the coating. Oxygen has a strong inhibitory effect on polymerization reactions. Therefore, to maintain a high polymerization efficiency of the photosensitive layer, a protective layer is coated on the surface of the plate to isolate oxygen.
The development process of the plate material after exposure by the plate-making machine is shown in Figure 2:
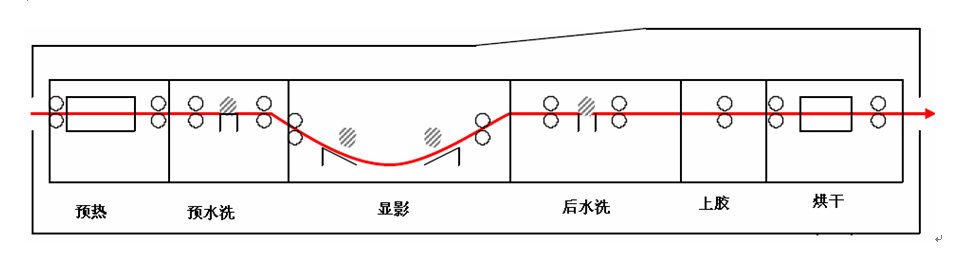
Figure 2 Photopolymerization CTP Plate Making and Development Process
As shown in Figure 2, pre-drying further solidifies the cured coating (image and text area) after exposure under high-temperature conditions, increasing the dissolution contrast between the image and text areas and enhancing the strength and printing resistance of the image and text areas.
The purpose of pre-washing is to remove the water-soluble oxygen barrier layer on the surface of the purple laser CTP plate before development. The water pressure and quantity of pre-washing spray should ensure that the protective layer can be completely removed to avoid affecting the next development process (the residual protective layer will affect the penetration of the development solution into the photosensitive layer).
The developer removes non-solidified areas in the developer solution through a developer brush, producing an image.
Post washing is to clean the printing plate that comes out of the developing tank to ensure that the layout is clean and free of residual developer.
The final gluing has two functions: to maintain the hydrophilicity of the base and avoid oxidation and dirtiness of the base to neutralize the alkaline residue in the layout to avoid its continuous effect on the graphic and text areas, causing changes in the print resistance.
The printing is dirty due to the quality of the 2 plates
The problem of dirtiness during the printing process is sometimes caused by issues with the quality of the plate material, mainly manifested as substrate treatment and defects in the photosensitive layer.
2.1 Basic processing
The purple laser CTP plate is composed of an aluminum plate base, a photosensitive layer, and a protective layer. Before applying photosensitive adhesive to the plate, the aluminum plate needs to undergo pre-treatment, mainly including three steps: electrolytic sanding, anodizing, and hole sealing.
(1) Electrolytic and order
The purpose of electrolysis is to form a sand mesh on a smooth aluminum plate, so that the graphic and textual parts of the printing plate have a good adsorption foundation, and the nongraphic and textual parts can be uniformly wetted by water, thereby forming a closed water film layer.

Figure 3 Morphology of sand under an electron microscope
As shown in Figure 3, the sand layer of the aluminum plate is composed of countless convex peaks and concave valleys, and the top shape of the sand convex peaks is generally smooth and mostly on the same plane; The concave valleys of the sand order are deeper, and of the valleys are also on the same plane. The side walls from peak to valley are relatively steep. This structure allows the layout to store enough moisture, and the blank areas of the printing plate are not easily dirty during printing. If the convex peaks are too high, the concave valleys are too deep, and the side walls are too steep, it is not easy to evenly coat the photosensitive adhesive. After exposure and development of CTP plates, the protruding peaks of the sand mesh are often difficult to ink due to the lack of photosensitive layer coverage. Even if the peaks with high sand mesh have sufficient photosensitive layer coverage, they will quickly be worn by the rubber cloth roller, water roller, and landing roller, causing printing faults in the "pattern plate". However, the sunken valley may cause incomplete development due to being too deep, leaving photosensitive resin in the blank area of the printing plate, resulting in dirt on the plate during printing.
A printing plate with an ideal sand mesh state, when printed on the machine, contains sufficient plate lubricant, does not easily get dirty, has good dot reproducibility, and has high printing resistance. According to the information, to ensure the normal transfer of offset ink, the water storage capacity of the printing plate needs to be maintained at 1.25 ml/m2. To maintain such water storage capacity, the distance between adjacent sand grains on the printing plate should be maintained at approximately 3um. If the distance between adjacent sand grains is greater than 3um, the sand grains on the printing plate are relatively coarse. Although the water storage capacity is high, the water on the printing plate will be carried away by the high-speed running rubber drum, reducing the water storage capacity of the printing plate and causing dirt on the blank area of the printing plate.
(2) Anodization
The purpose of anodizing is to generate an AI2O3 film layer on the surface of the aluminum plate substrate, improving the printing resistance of the plate and the hydrophilicity of the nongraphic parts. The thicker the oxide film, the stronger its wear resistance. However, if the thickness of the oxide film layer increases, the elasticity of the film layer will decrease and the rigidity will increase, making the film layer brittle and prone to cracking during high-speed printing, resulting in dirty printing plates. If the oxide film is too thin, the wear resistance will decrease. During the printing process, sand particles are prone to wear and tear, causing a decrease in the water retention of the blank part of the printing plate and resulting in dirty printing.
(3) Sealing holes
After electrolytic treatment, there will be uniform and deep sand particles on the plate base. If photosensitive adhesive is directly applied at this time, the plate surface will adsorb the photosensitive adhesive too firmly, and the photosensitive layer cannot be completely detached after development, making the nongraphic and textual parts of the printing plate oleophilic and prone to getting dirty during printing. Therefore, sealing treatment should be carried out to reduce the sensitivity of sand particles.
Sealing treatment refers to the use of the sealing solution to fill the micropores on the aluminum substrate before applying the photosensitive liquid. The main factors affecting sealing are the sealing process, water quality, concentration, temperature, and sealing time of the sealing solution. Insufficient or excessive sealing of holes will have a serious impact on the printing suitability of the plate material. The high concentration and temperature of the sealing solution in the sealing tank are conducive to sealing the holes. The corresponding CTP plate material is exposed and developed, and the ground is clean. It is not easy to produce "dirt" during printing, but the printing resistance is low. On the contrary, insufficient hole sealing can easily to serious "bottom residue" of the plate base, resulting in dirty printing problems.
2.2 Photosensitive layer
In the production process of purple laser plates, there is a high requirement for the cleanliness of the production environment. If there are suspended particles such as dust in the air, they will create blue spots on the plate adsorbed during coating. Once the plate is mounted on the machine, it will form point-like dirt on the blank part of the plate.
Due to the high sensitivity of the photosensitive layer, purple laser CTP plates require strict transportation, storage, and usage conditions, and have a certain shelf life. For example, it requires to be placed in a sealed packaging box before exposure, in a dry and cool environment, and can only be opened under safe light. The shelf life of the plate material is generally about one year. If the fruit plate material exceeds the shelf life or accidentally exposes the CTP plate material without being detected, the hydrophilicity of the blank part of the plate after plate making and development will be affected or there will be coating residue on the blank part, causing the plate to be dirty after machine printing. Therefore, the transportation, storage, and use of purple laser CTP plates must be strictly operated by standard requirements. For fully automatic plate loading equipment, attention should be paid to checking the light avoidance of the equipment.
Dirty printing caused by the development process of 3 plates
The development process of the purple laser CTP plate is different from that of the PS plate and thermosensitive CTP plate. The development process is divided into the following steps:
Exposure → preheating → water washing → development → water washing → gluing → printing plate
Each step in the development process will have an impact on the processed printing plate.
3.1 Preheating
Preheating (pre-drying) further solidifies the cured coating (image and text area) after exposure under high-temperature conditions, increasing the dissolution contrast between the image and text areas and enhancing the strength and resistance of the image and text areas. At present, the manufacturers of purple laser CTP plates on the market will put forward corresponding preheating temperature requirements. For example, the recommended preheating temperature for Huaguang PPVS purple laser CTP plates is 99-110 ℃. If the temperature is too low, the printing resistance of the produced plate will be affected. If the temperature is too high, it will cause local sticking of the plate, which will result in local dirt or darkening of the plate after installation, as shown in Figure 4.

a. Normal branch b. High-temperature paste plate
Figure 4: Excessive preheating temperature causing plate sticking
3.2 Development
The purple laser CTP plate is a photopolymerization-type negative image plate material. The development during post-processing is mainly affected by factors such as the pH value, temperature, development time, and pressure of the development brush of the development solution. During the development process, the low pH value of the development solution, low temperature of the development solution, short development time, and too small pressure of the development brush can all to insufficient development, resulting in incomplete removal of photosensitive glue in the nonimage and text areas, and causing the printing plate to become dirty.
(1) It is to use a development solution that matches the plate material to achieve the development effect. During use, the amount of supplementary solution should be reasonably set according to the requirements, and the developer should be replaced promptly according to the development capacity and lifespan of the solution to avoid aging and pH decline, maintain the development effectiveness of the developer, and ensure development quality. If the pH value is too low, it may cause a "background" after development, and the printing plate may become dirty after being put on the machine.
(2) The development temperature and development time of the plate material should be controlled within a certain range, because as the temperature of the development solution decreases, the development performance of the development solution also significantly decreases, and the ability to dissolve the photosensitive layer decreases, resulting in insufficient development. If the development time is too short, it can also cause insufficient development, resulting in a normal increase in the percentage of dots in the graphic and text parts, and even causing the photosensitive layer to remain in the blank part, causing the blank part to become dirty; However, if the temperature is too high and the development time is too long, it will cause the exposed image and text to dissolve, resulting in the loss of fine dots and a decrease in dot restoration and printing resistance. Moreover, higher development temperatures will corrode the hydrophilic layer of the printing plate and affect its hydrophilicity, making it prone to getting dirty during operation.
(3) The purple laser CTP plate needs to be wiped with a brush during the development process to enhance the development effect, and the pressure of the brush on the plate directly affects the development effect. If the brush pressure is too small, it can cause incomplete removal of the photosensitive layer in the blank part of the plate, resulting in printing dirt.
(4) The maintenance and upkeep of the developer is very important, especially paying attention to regularly cleaning the residue in the tank and on the tube wall. If there is too much dirt, oxalic acid can be mixed with water to remove it. At the same time, the brush roller should also be inspected and cleaned. If it is severely worn, it should be replaced promptly. In addition, it is necessary to regularly check the circulation system, replace the developer filter element promptly, and pay attention to whether there are errors between the actual values and settings of the developer temperature and time.
3.3 After washing with water
Because the development solution used in the purple laser CTP version is mainly composed of surfactants, compared to ordinary positive PS and thermosensitive versions, the layout is more prone to getting dirty due to residual surfactants. Adequate post-washing water pressure and amount of water can thoroughly remove residual surfactants from the plate, avoiding dirt on the plate material.
3.4 Protective glue
The two functions of back gluing are to neutralize alkaline residues in the layout and avoid their continuous impact on the graphic and text areas, resulting in changes in the printing resistance; Maintain the hydrophilicity of the substrate to avoid oxidation and dirtiness. Be sure to keep the glue roller clean during the gluing process, otherwise the printing plate may be dirty.
Improper application of protective glue can also cause dirt on the printing plate. If a low concentration of glue is used during gluing, the amount of protective glue applied is not enough to truly protect the printing plate, resulting in oxidation reactions in nonimage parts, or excessive loss of moisture in the sand layer of the printing plate, poor water retention, and dirty printing plate. If the protective glue is applied unevenly, thick, thin, and sometimes there are obvious adhesive channels, it can cause dirt on the printing plate. So the amount of protective glue applied must be appropriate and even to truly protect the printing plate.
3.5 Revision
The purple laser CTP plate material can be used to repair the residual coating or stains on the plate with a plate repair pen. It is recommended to use the BASE-LINE CTP-1000 revision pen or the revision pen recommended by the plate manufacturer.
Revision should be done after the layout is dry. After revision, the revision solution should be wiped clean promptly. If the revision solution stays on the base for too long, the hydrophilic layer in the blank area will be damaged, causing dirt on the revision area. When wiping off the repair solution, be careful not to bring it to other parts of the layout to avoid residual repair solution and damage to the hydrophilic layer. After the revision, protective glue should be applied to the revision area promptly.
4 Conclusion
The above analyzes the possible causes of printing dirtiness from the quality of purple laser CTP plates, plate development, and printing process. In practical applications, if dirtiness occurs, only gradual investigation and careful analysis are needed to quickly find and solve the cause of dirtiness, improving work efficiency.